
KNOWPIA
WELCOME TO KNOWPIA
Summary
A partial solar eclipse occurred on August 20–21, 1971. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth. It was visible near sunrise on August 21 over parts of Australia.
| Solar eclipse of August 20, 1971 | |
|---|---|
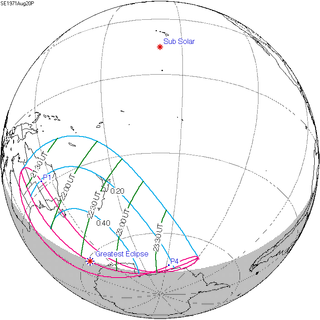 Map | |
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Partial |
| Gamma | −1.2659 |
| Magnitude | 0.508 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Coordinates | 61°42′S 135°24′E / 61.7°S 135.4°E |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 22:39:31 |
| References | |
| Saros | 154 (4 of 71) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9445 |
Related eclipses edit
Solar eclipses of 1968–1971 edit
This eclipse is a member of a semester series. An eclipse in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.[1]
| Solar eclipse series sets from 1968 to 1971 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ascending node | Descending node | |||||
| Saros | Map | Gamma | Saros | Map | Gamma | |
| 119 | 1968 March 28 Partial |
−1.03704 | 124 | 1968 September 22 Total |
0.94507 | |
| 129 | 1969 March 18 Annular |
−0.27037 | 134 | 1969 September 11 Annular |
0.22014 | |
| 139 | 1970 March 7 Total |
0.44728 | 144 | 1970 August 31 Annular |
−0.53640 | |
| 149 | 1971 February 25 Partial |
1.11876 | 154 | 1971 August 20 Partial |
−1.26591 | |
| A partial solar eclipse of July 22, 1971 occurs in the next lunar year set. | ||||||
References edit
- ^ van Gent, R.H. "Solar- and Lunar-Eclipse Predictions from Antiquity to the Present". A Catalogue of Eclipse Cycles. Utrecht University. Retrieved 6 October 2018.
External links edit
- Earth visibility chart and eclipse statistics Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC
- Google interactive map
- Besselian elements
Wikimedia Commons has media related to Solar eclipse of 1971 August 20.


